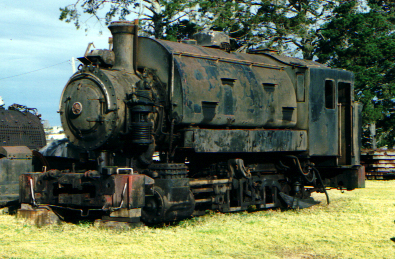
|
Badger Australian Iron & Steel shunter |
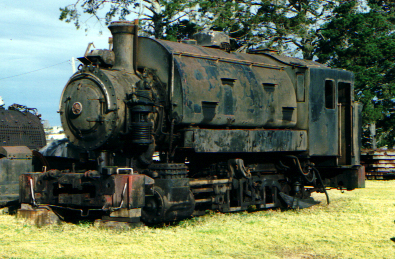
This photo is courtesy of Mark Newton and shows Badger at Dorrigo in 1999, stored in black oil for weatherproofing.
The loco is propped on blocks, with the wheels and motion stored nearby.
This locomotive was built by Australian Iron & Steel, Port Kembla for shunting duties under steelworks capacity increases during World War 2. It was one of a class of eight chunky 0-6-0ST locomotives comprising the pattern locomotive "Bandicoot" built by H. K. Porter to a classic US design, followed by four local-built copies from Clyde Engineering and three wartime examples built by the AIS at their own workshops. The class members were:
| Name | Builder b | Comments b |
|
Bandicoot
|
H. K. Porter 7160 of 1929 |
In service November 1929 Withdrawn 14-12-1971 Scrapped 22-1-1975 |
|
Brolga
|
Clyde Engineering Co No.455 of 1936 |
In service December 1936 Withdrawn 2-8-1971 Scrapped 19-2-1975 |
|
Bronzewing
|
Clyde Engineering Co No.457 of 1937 |
In service February 1937 Withdrawn 16-12-1971
|
|
Baradine
|
Clyde Engineering Co No.460 of 1938 |
In service June 1938 Withdrawn 19-12-1971 Scrapped 19-2-1975 |
|
Burrawa
|
Clyde Engineering Co No.461 of 1938 |
In service October 1938 Withdrawn 17-12-1971 Scrapped 22-1-1975 |
|
Bellbird
|
AIS Port Kembla, 1943 |
In service August 1943 Withdrawn 19-12-1971 Scrapped 19-2-1975 |
|
Badger
|
AIS Port Kembla, 1943 |
In service November 1943 Withdrawn 18-12-1971 Scrapped 8-1-1975 |
|
Bantam
|
AIS Port Kembla, 1944 |
In service February 1944 Withdrawn 19-12-1971 Retained for preservation bearing Badger's nameplates. |
Photos suggest the first two engines Bandicoot & Brolga carried ornate Porter-style steam & two sand domes atop the saddle tank, giving the locomotives a very US-look, whereas the following engines carried only an undecorated steam dome. c
These eight locomotives were employed on heavy shunting duties around the AIS Port Kembla steelworks. Late in their careers they came to dominate the molten slag transfer and tipping trains, as these used a steam operated tipping mechanism which the early . With the arrival of more diesel locomotives the tipping mechanisms were finally converted to compressed air operation, leading to the withdrawal of Badger and its sisters in late 1971.
After a period in storage at the steelworks, the majority were cut up by AIS for steelworks scrap in early 1975. The exceptions were Bronzewing, which was donated to the NSWRTM, and the locomotive now known as Badger, which was retained for intended display at the AIS visitors centre at Coniston. (Ken McCarthy's "Gazetteer of Industrial Steam Locomotives, Illawarra District NSW" lists this loco as actually being Bantam, but carrying 'Badger's' nameplates.)
Rather than being placed on display at the AIS visitors centre at Coniston, Badger / Bantam was acquired by the Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum and transferred to their Rhondda Colliery storage site in 1978. It was subsequently relocated to Dorrigo in the 1980's where it remains in storage with the Dorrigo collection, awaiting the day this museum opens to the public.
References
| a |
Kramer, J. 'The Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum - an Illustrated Guide', published by the Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum, 1987. Printed by North Coast News Pty Ltd, 53 Moonee St, Coffs Harbour 2450 NSW. |
| b | McCarthy, K. 'Gazetteer of Industrial Steam Locomotives, Illawarra District NSW', prepared by K. McCarthy for the Illawarra Environmental Heritage Committee. Published by the Australian Railway Historical Society (NSW Division) December 1983. |
| c | Webmaster's observation or comment. |
Page updated: 31 July 2012
|
Government Railways: |
|
Contributions | ||||||||
|
Private & Industrial Railways: |
|
Copyright |